Introduction to design automation for manufacturing
- Introduction
- What is design automation?
- What are the advantages of design automation?
- Integrating design automation with CAD workflows
- Integrating design automation with CAM tools
- Why would I need design automation in a manufacturing environment?
- How can design automation be applied in the real world?
- Looking ahead: The future of design automation
- Could design automation help your business?
Introduction
In today's rapidly-evolving manufacturing landscape, innovation isn't just advantageous – it's necessary. Staying at the forefront of the industry requires constant adaptation and creative solutions to meet ever-changing market demands. One transformative force making an impact in the industry is design automation – an approach that redefines how products are designed.
In this article, we'll examine the role of design automation in modern manufacturing, discussing its essential concepts and applications, and its impact on enhancing production efficiency, agility, and quality. We'll investigate its integration with CAD (Computer Aided Design) and CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) systems, its practical use in 3D printing and CNC machining, and present real-world examples of its success in commercial manufacturing.
We’ll also explore how design automation streamlines manufacturing workflows, boosts efficiency, and enables easier customization, which in turn results in superior products and significant time and cost savings compared to traditional design approaches.
Key takeaways:
-
Design automation is a crucial innovation in modern manufacturing
-
It simplifies and accelerates the design phase using software, reducing manual tasks and errors
-
Benefits include increased efficiency, faster product deployment, better customization, and improved product quality
-
It integrates with CAD and CAM systems, particularly useful in 3D printing and CNC machining
-
Real-world examples showcase its practical applications, from inductor design to automotive production
-
The future of design automation includes AI integration, customization, sustainability, and more
-
Design automation benefits both CAD novices and experts, streamlining workflows and reducing design costs

What is design automation?
The design phase of any product is critical in shaping its functionality and determining its production costs. Efficient design is essential for a successful manufacturing process and will impact every stage of a product's lifecycle.
Traditional CAD processes, while effective and still relevant in the manufacturing industry, come with their own complex challenges. For instance, CAD design for commercial products comes with a steep learning curve that can take years to master. Manual design steps in CAD can be time-consuming, error-prone, and often lack flexibility to adapt to fast-changing manufacturing demands and shorter product life-cycles. Such limitations can result in delays, higher costs, and a diminished competitive edge in the market.
Design automation offers a powerful solution to address these challenges. It uses software to automate design tasks that are traditionally performed manually in CAD software. Powerful algorithms operate within a set of predefined rules, which can be applied to everything from simple components to complex assemblies. The goal of design automation is to reduce repetitive manual tasks, eliminating errors and accelerating the design phase, ultimately contributing to a more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process.
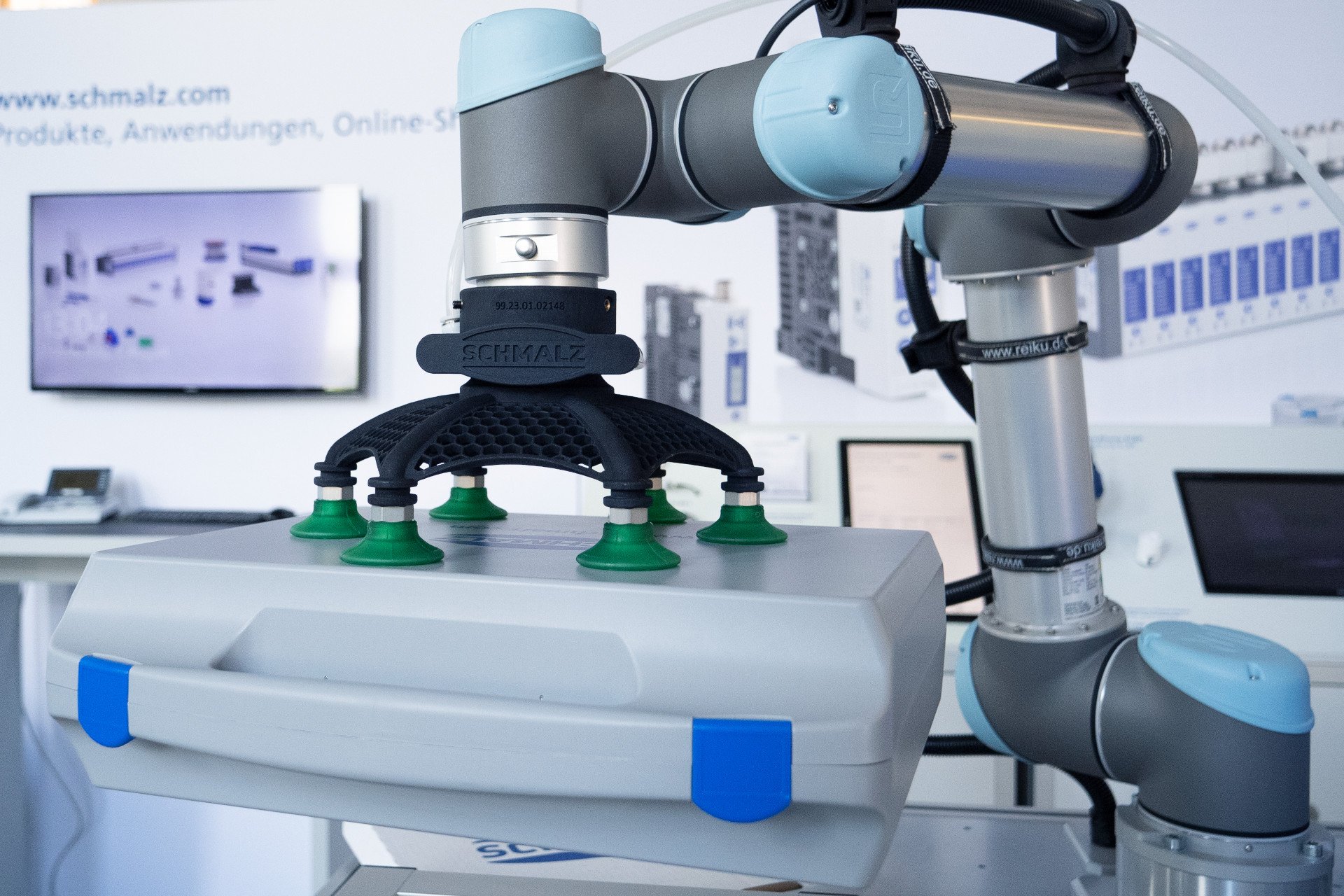

Using design automation, an assembly such as this robot gripper can be reconfigured to different applications quickly, without manual CAD work and CAD expertise
Just as AI tools like ChatGPT can accelerate writing and editing processes or allow those without artistic skills to create realistic-looking images, design automation can streamline a design process and empower those without CAD skills to create designs that meet industrial standards.
It’s not just limited to CAD novices, however – there are many useful features of design automation software for experienced CAD users as well. For instance:
-
It can manage repetitive manual CAD tasks using rule-based algorithms, so the timeframe from initial concept to final product is significantly reduced.
-
It can pull large amounts of metadata from external sources and integrate this into a design to customize it to unique requirements, without the need for a dedicated design engineer.
-
It can improve product quality by maintaining precision and consistency, facilitating rapid design changes without multiple separate operations in CAD software.
On a higher level, design automation has the potential to revolutionize entire business models, opening possibilities for mass-customization and making complex design processes more efficient.
Below are some examples from the commercial manufacturing sector that demonstrate the practical application of design automation:
Example 1: Quickly define the height, diameter, and number of turns of an industrial inductor coil
This interface, with its user-friendly number input fields, enables anyone, including customers, to easily adjust a pre-configured base design according to their specific requirements.
The interface's configurable nature allows for varying levels of complexity, catering to different user skills. Being web-based, it can be readily deployed on customer-facing webpages.
Example 2: Specify vacuum gripper contact points on complex-shaped objects with a few mouse clicks
Reconfiguring assemblies that have a large amount of components can occupy a significant amount of manual design work in CAD.
Design automation can streamline this process, in this case, instantly creating an optimized vacuum gripper assembly that grips an irregular geometry at selected points. This saves a great deal of manual CAD work, and makes the gripping process more reliable.
Example 3: Design tailored medical devices quickly
Patient-specific devices require patient data to be collected, interpreted, and manually modeled. Design automation can take this input data and apply it to a base design, making a customized device in seconds.
What are the advantages of design automation?
Many believe that the main advantages of design automation lie in perfecting the final product and simplifying customization. While this is true, the real efficiency gains come from automating the steps in-between.
Designing manufacturing aids might not sound exciting, but it's a process that typically takes up a lot of design time and effort. This is a huge business expense, and automating parts of this process can significantly improve the time and cost involved in design and make life easier for everyone involved in the process.
Take, for example, fixture design in the manufacturing industry. These custom workholding devices hold, locate, and position workpieces during manufacturing operations. Design automation for fixtures allows CAD designers to design parts much faster and with higher accuracy than traditional methods. It also broadens the group of participation by eliminating the need for extensive CAD training, so non-CAD experts can be onboarded into the process. This approach fosters a diverse range of perspectives, shortens feedback loops between departments, and enhances collaboration and efficiency within business operations.
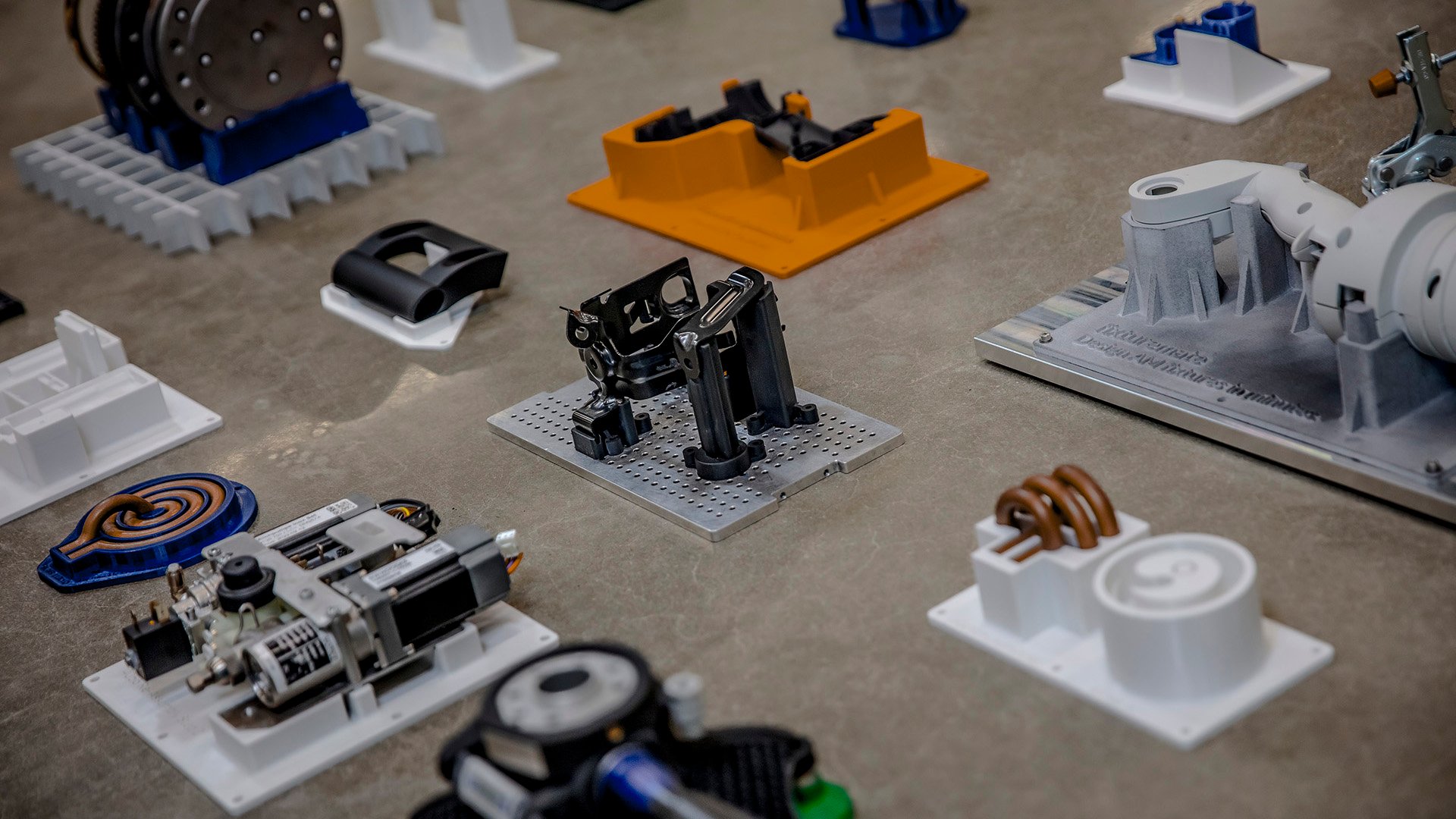
Design automation can be applied to many areas of manufacturing
Integrating design automation with CAD workflows
CAD systems like SolidWorks, CATIA, and AutoCAD offer a wealth of features, but with this comes complexity. Mastering these tools for effective commercial use typically takes years of training and practice. Despite CAD’s status as an indispensable industry tool, user operations can be repetitive and time-consuming, even for experienced CAD professionals.
Design automation is a solution that streamlines these complex sequences of steps into a single step. Organizations can set up rules, constraints, and user interfaces tailored to their individual needs. This means designs created in any standard CAD system can be imported into a customized user interface, which simplifies the more complex aspects of a typical CAD interface.
This streamlined approach not only allows the primary design team to focus on higher-priority and creative tasks but also enables those without extensive CAD skills to create industrial-standard designs. These designs still adhere to critical product specifications, thanks to rule-based algorithms.

Design automation applications such as fixturemate streamline design by automating manual CAD operations
Integrating design automation with CAM tools
With the ability to manufacture prototypes and end-use parts locally, designs can be evaluated, improved, and iterated on within a matter of hours, leading to an improved product development process and shorter production cycles than traditional fabrication workflows usually allow.
Digital manufacturing methods such as 3D printing and CNC milling can manufacture increasingly complex geometries and are ideal for small scale production. 3D printing is particularly accessible in terms of ease of use and cost. To get started, you just need two things: a 3D printer and a design for 3D printing.
While there have been considerable improvements in 3D printer technology in recent years, the development of tools to simplify design for 3D printing has not kept pace. This is where design automation comes in. It bridges this gap, so companies can quickly adopt 3D printing using a low-cost 3D printer and a design automation solution.
The effectiveness of this approach has been demonstrated by automotive manufacturers who use it to design manufacturing aids, like fixtures. These highly customized tools enhance both efficiency and working conditions on the factory floor. Combining design automation with 3D printing opens a world of innovation in manufacturing.
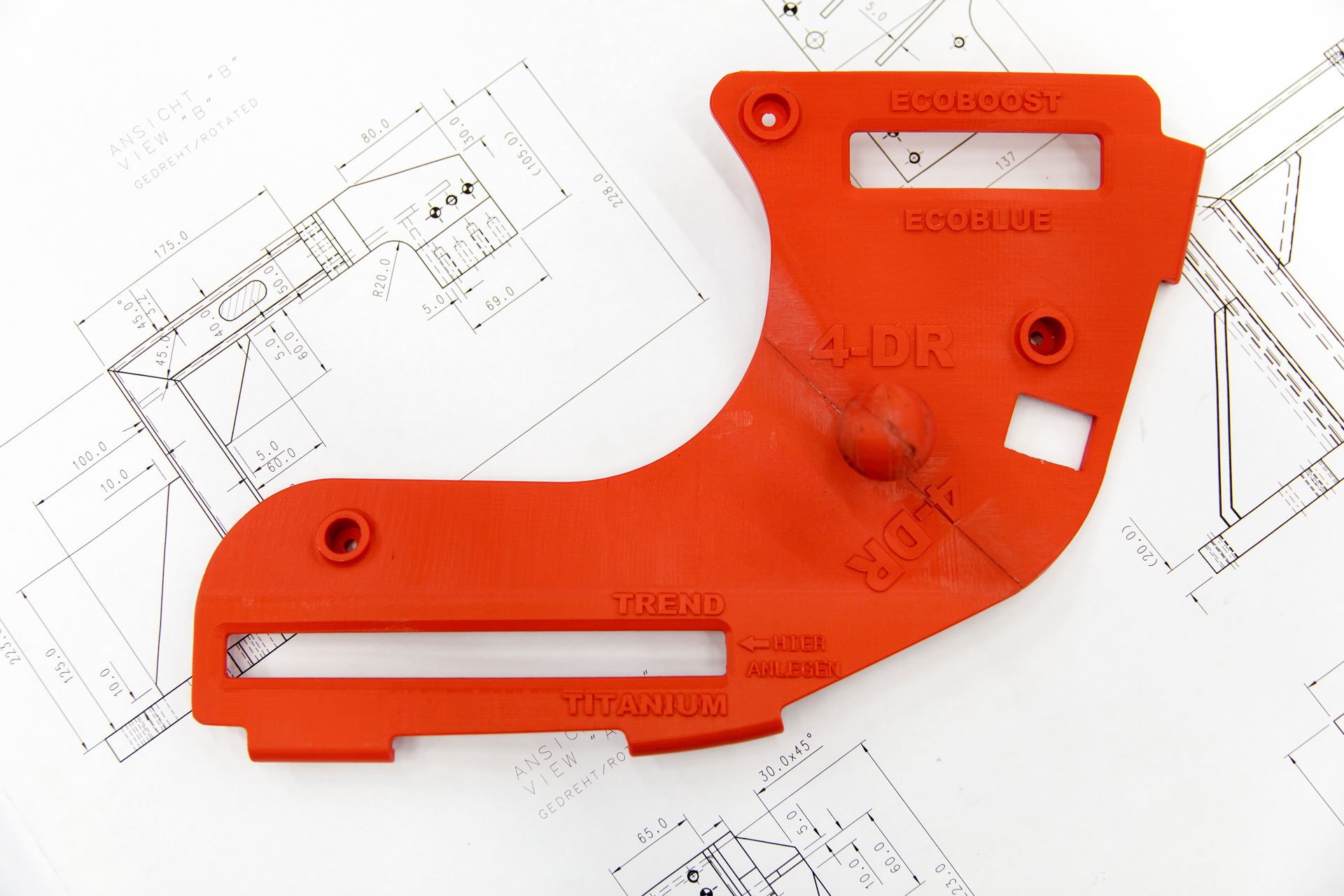

Ford Motor Company's 3D printed tool for decal alignment on the workfloor
Why would I need design automation in a manufacturing environment?
Design automation is a strategic asset that addresses multiple challenges in the manufacturing environment. Depending on the industry, product category and production environment, design automation can offer various advantages, which will be differentiated briefly here:
Frictionless processes with more flexibility and less waste
Applied correctly, design automation creates a flexible design workflow with minimal friction, a crucial factor in an industry where efficiency is key. This increased efficiency plays a key role in reducing waste, aligning well with lean manufacturing principles, which aim to eliminate waste in its various forms, such as defects, excess processing, overproduction, and time spent waiting – in this case, for designs to be ready.
Improved productivity and faster deployment
By significantly speeding up the design process, design automation allows for more rapid development and deployment of products. This acceleration is especially beneficial in fast-paced manufacturing sectors where responding swiftly to market demands or changes is essential.
Better potential for customization
In today's market, the demand for personalized and bespoke products is rising, and manufacturers must adapt to this trend. Design automation facilitates this adaptation by allowing for greater customization without compromising production efficiency or scalability.

Designs can be evaluated, improved, and iterated on within a matter of hours when design automation is paired with 3D printing
Quality improvements
Manufacturers are continually seeking ways to enhance efficiency, precision, and the quality of their products. Design automation serves as a tool to achieve these goals. In an environment where innovation is the key to staying ahead, design automation provides a platform for continual improvement and optimization of manufacturing processes.
Bridging the labor gap
One of the significant challenges in traditional design processes is the skilled labor shortage and the need to upskill existing personnel. Design automation addresses this issue by simplifying complex processes, making it easier for less skilled workers to perform tasks that would otherwise require extensive training. This aspect of design automation not only helps in bridging the skills gap but also reduces the time and resources spent on training, thereby optimizing human resource deployment.

A broader group can engage in the design process through design automation – including those who have never used CAD before
How can design automation be applied in the real world?
Most of the time, design automation simplifies the design process through an intuitive interface. Users find a design template which has been pre-defined with degrees of freedom. While in some scenarios there is only minor adaptation and fine-tuning needed, in other scenarios the full design process is available for the user to steer – the software application facilitates the guidance and assistance.
The interface works within specific rules and constraints, such as dimensions or component relationships, while real-time adjustments are effortlessly made through sliders, input fields, and checkboxes, so designs can be dynamically adapted in real time.
While at first glance these options for the user to influence may seem limited, such processes can easily become more extensive. For example, applications in the context of medical cases often start with the upload of patient-specific scan data, which determines all subsequent design steps.
In the context of fixture design, the original CAD file of a workpiece serves as the foundational blueprint from which a fixture is created. The intent of a fixture is to securely hold and position a workpiece during assembly or measuring operations. Design automation simplifies the design process, so tailored fixtures can be produced rapidly. Using design automation tools like fixturemate, users can execute typically complex operations like boolean subtractions, offsets, text labels, holes, and more, with just a few simple clicks.
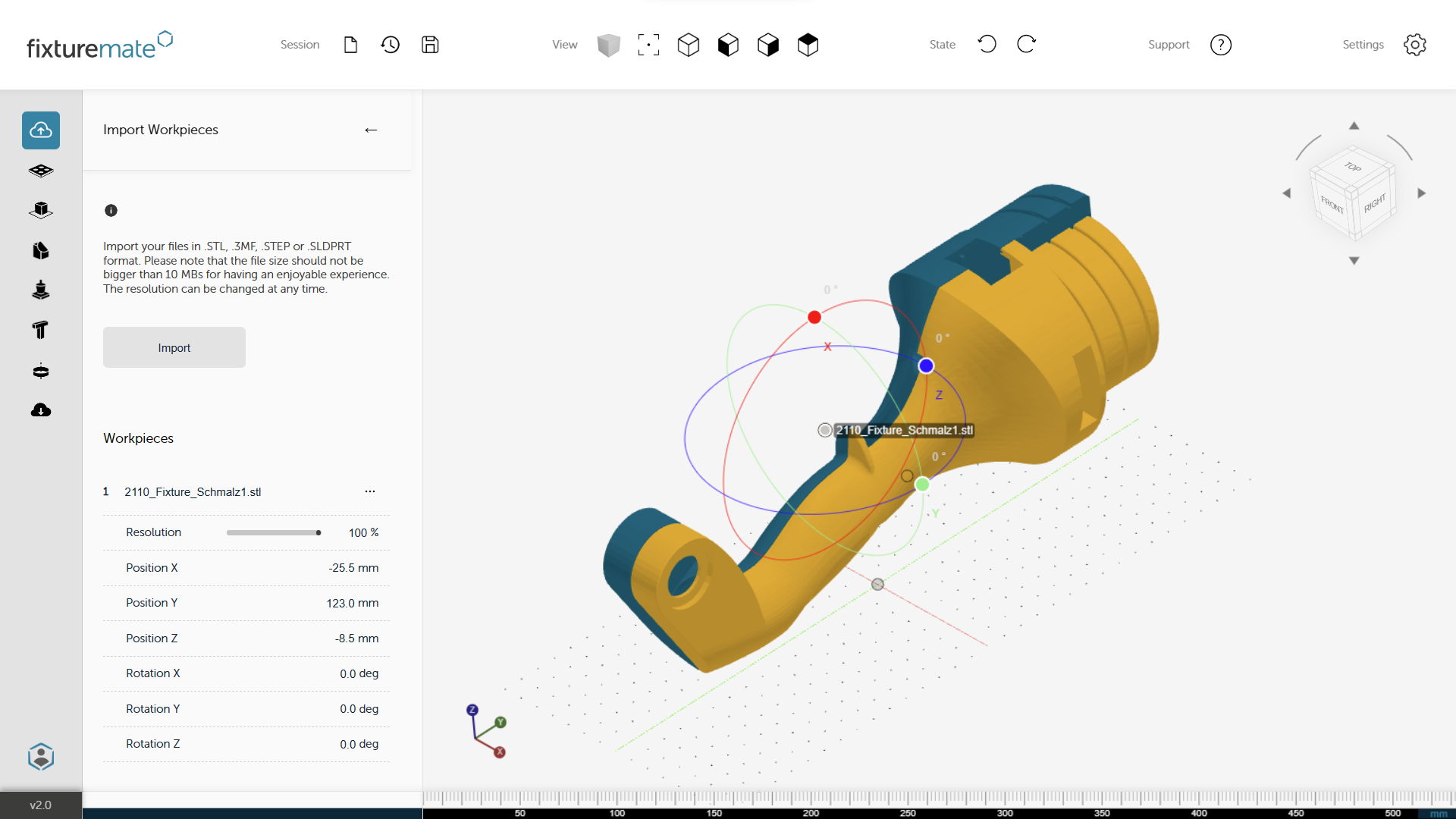
fixturemate is design automation software that streamlines the time-intensive task of fixture design
Use case: An automated design approach for custom copper inductors
PROTIQ, an expert in producing copper inductors for induction heating, embraced design automation to overcome the inefficiencies of traditional CAD processes in manufacturing. Initially, the manual and repetitive CAD tasks were too time-consuming and costly, making the production of precisely adapted inductors for metal workpieces challenging. By integrating an inductor configurator with trinckle's paramate engine, PROTIQ revolutionized their approach. This configurator offers about 20 adjustable parameters for customizing inductor geometry, while ensuring functionality and printability. Hosted on a user-friendly web application, it made the entire process viable by allowing customers to easily design and order custom inductors, bypassing the complexities of CAD or Design for Additive Manufacturing expertise. This automation not only streamlined production but also opened up new possibilities for efficient and scalable manufacturing.
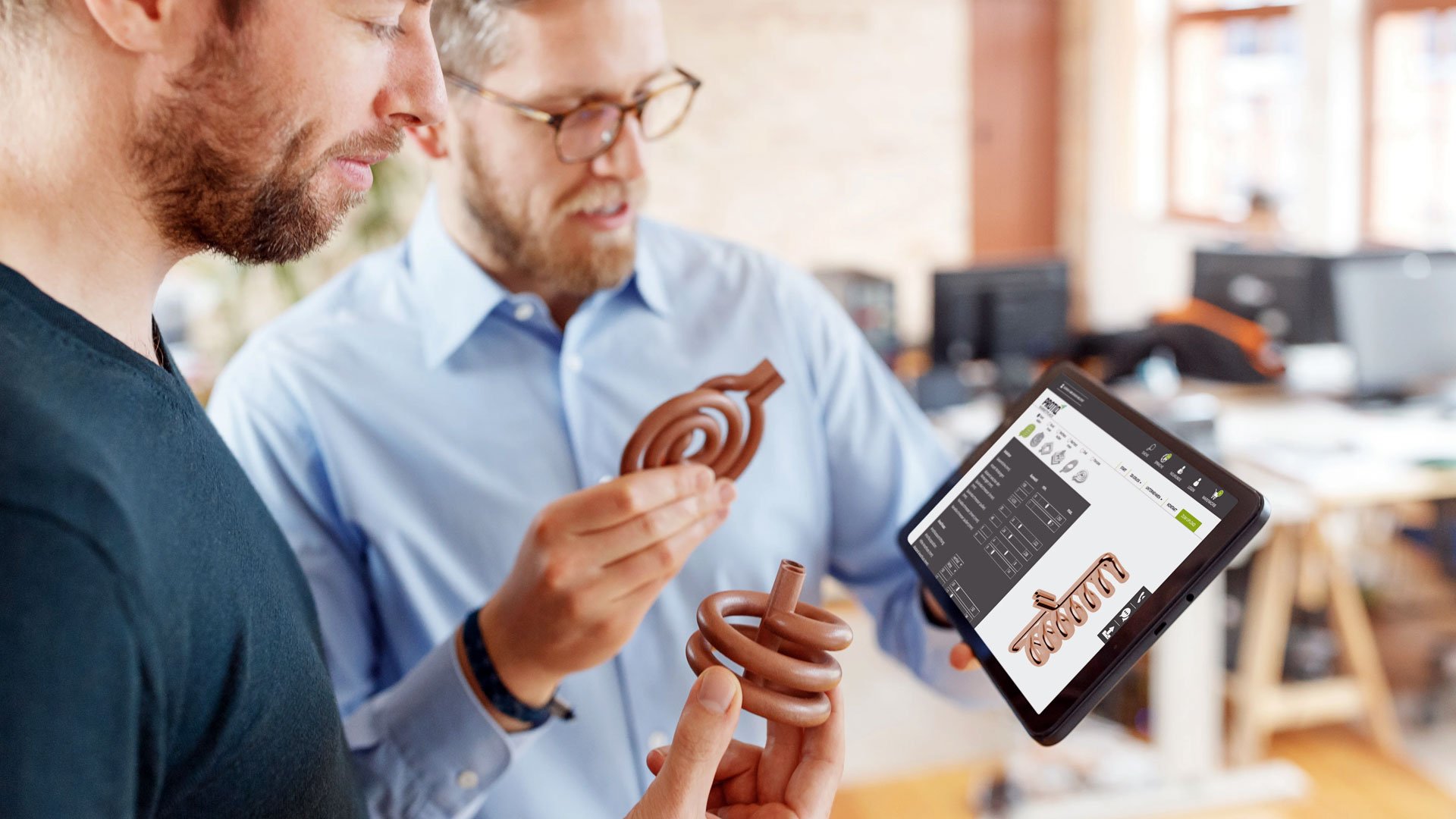

PROTIQ's configurator offers 20 adjustable parameters for customizing inductor geometry, while ensuring functionality and printability
Use case: Optimize complex robotic assemblies in seconds
J. Schmalz GmbH streamlines vacuum gripper design with trinckle's paramate engine, transforming a day-long task into a 10-minute, user-friendly online process. This platform on Schmalz's website allows customers and employees globally to customize grippers by defining tasks and specifications, including 3D models, with intuitive guidance and algorithmic optimization. No CAD expertise is needed, and users receive a CAD model and quote quickly, ensuring designs meet specific automated industrial needs.
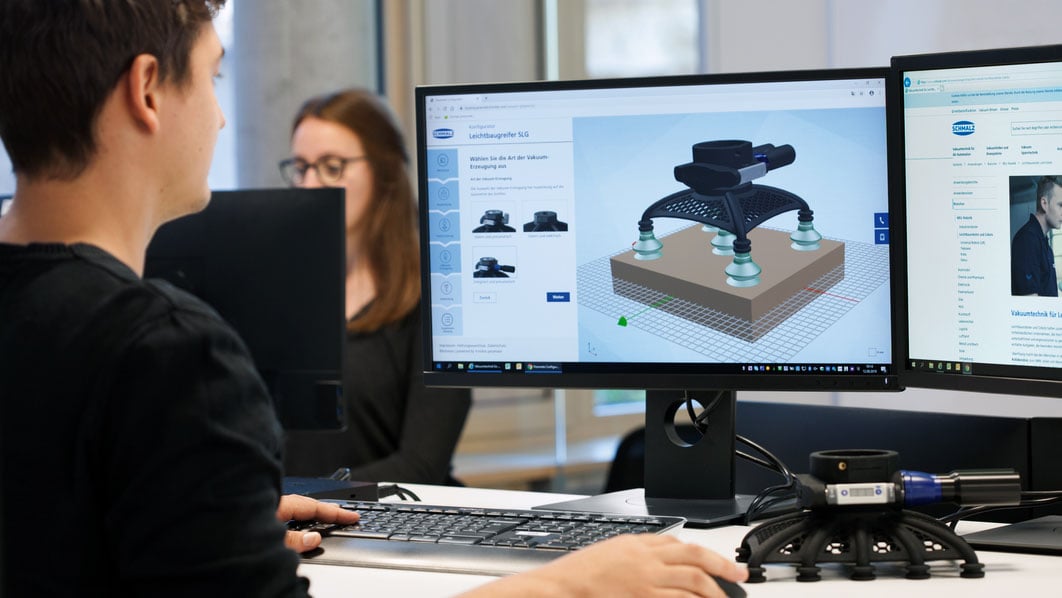

Combining user-friendly configuration, instant CAD model generation, and 3D printing, this approach reduces design time to mere minutes
Use case: Streamlining automotive production workflows
Ford Motor Company's adoption of design automation allows assembly line workers to design tools at the expertise level of CAD professionals, optimizing and deploying each tool in less than a week. This strategy not only reduces complexity and time in the design process but also enhances overall production efficiency.
Ford plans to expand this automation approach across its range of 3D printed tools, leveraging the many benefits of additive manufacturing to boost productivity in its manufacturing processes.
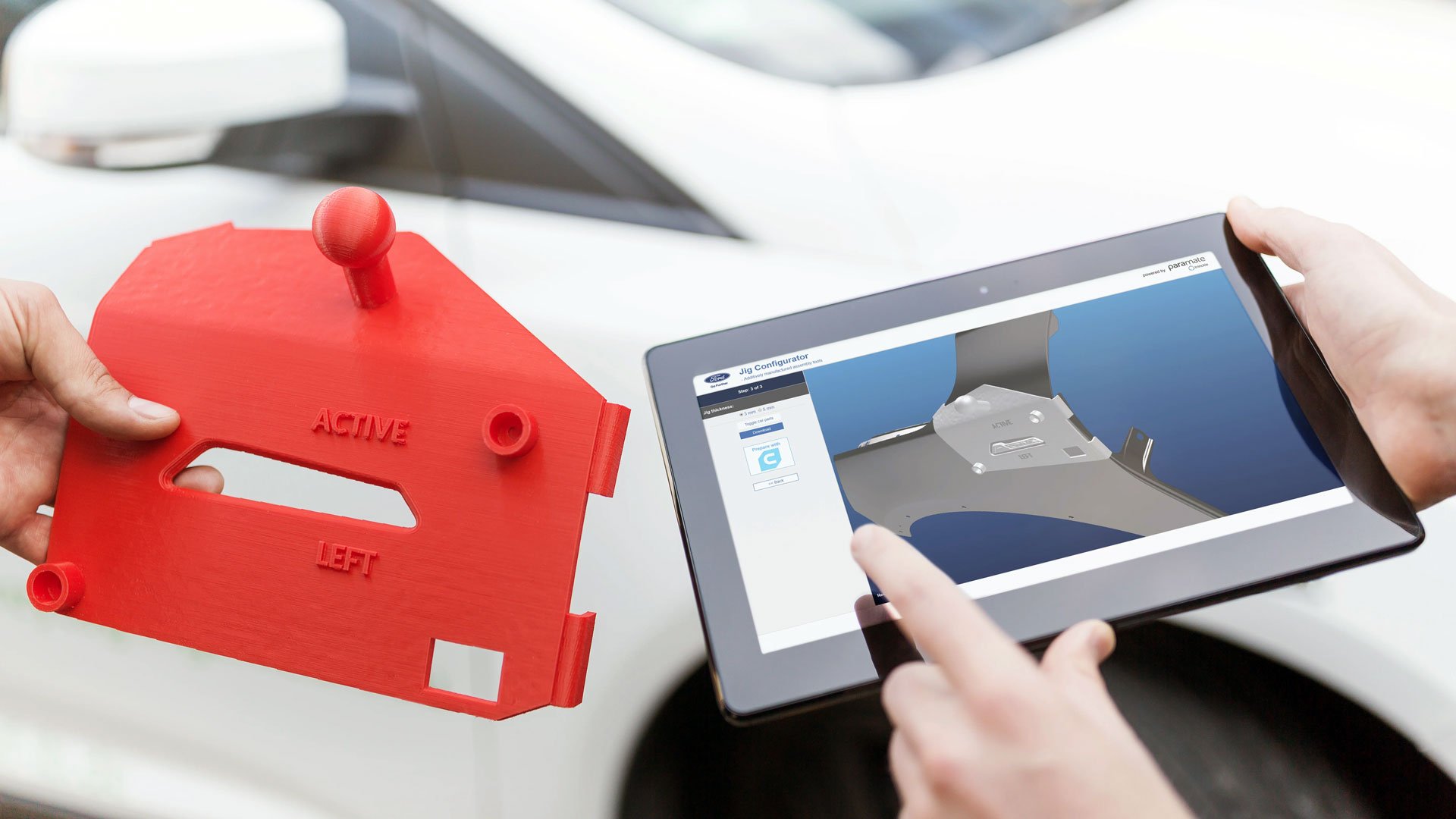

Ford has successfully integrated over 50 different 3D printed tools in its production, yielding immediate cost savings and efficiency gains
Looking ahead: The future of design automation

At trinckle, we predict design automation is poised to reshape the manufacturing industry in various ways:
Integration of advanced AI and machine learning. AI and machine learning technologies will become increasingly integrated into design automation, making it possible to anticipate and optimize designs based on a user’s requirements.
Customization and personalization. As people increasingly want products tailored just for them, design automation will become key in mass customized products without sacrificing production efficiency.
Improved collaboration tools. As remote work grows, design automation tools will evolve to support better collaboration across different locations, leveraging cloud-based platforms.
Enhanced user interfaces and experience. The focus will be on creating more intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that make design automation accessible to a broader audience.
Sustainability and material innovation. Design automation will increasingly incorporate environmental considerations, optimizing for reduced impact and integrating sustainable materials.
Adaptation to Industry 4.0 and IoT. Design automation will need to seamlessly integrate with Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and other advanced manufacturing technologies.
Greater simulation capabilities. Enhanced simulation within design automation will reduce the need for physical prototypes, speeding up product development.
Democratization of design. The widespread availability of design automation tools will empower smaller manufacturers and individual designers, democratizing the design process in manufacturing.
Responsive and adaptive design. Future tools could enable creation of designs that adapt to changing requirements during the manufacturing process.
Integration with digital twins. The use of digital twins will become more integrated with design automation, allowing for real-time optimization of both design and manufacturing processes.
Could design automation help your business?

Design automation is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, reducing design time and elevating product quality by maintaining precision and consistency. As we learned above, it's not just about speeding up processes; it's about transforming business models, allowing for mass customization and more efficient workflows.
To evaluate the potential for your organization you might want to separate benefits for CAD novices and CAD experts, and we’ve summarized the key benefits below:
CAD novices
-
Can design items to industrial standards easily, bypassing the steep learning curve often associated with CAD.
-
Are empowered to design products independently, adapting and modifying designs to improve workflow without always relying on design experts, thus reducing back-and-forth communication.
-
Don't have to worry about errors, as rule-based algorithms ensure the accuracy of the products they design.
-
Can quickly and independently reconfigure existing designs to meet their individual needs, such as better ergonomics.
-
Can work within intuitive interfaces that are customized by design experts to meet specific business requirements. This approach simplifies the process for those with limited experience, allowing them to effectively understand and use CAD tools and contribute to design projects without needing extensive training.
-
Can learn and apply fundamental design principles more quickly, boosting their practical experience and confidence in managing design projects.
-
Applies to internal CAD novices and your organization’s customers alike.
CAD experts
-
Can define rule-based algorithms that ensure a specific design standard. Can also configure simplified design interfaces, making it easier to onboard CAD novices into the design fold. This shifts the responsibility of low-priority CAD tasks to others. This claimed back time can then be used for higher-priority creative design tasks.
-
Can streamline repetitive manual CAD tasks, reducing the amount of time-consuming CAD operations it takes to realize a design concept, in turn reducing design costs for the business.
-
Can quickly mass-customize products using an automated workflow, avoiding intricate design work, e.g. surface modeling to make customized geometry.
-
Can get products to market faster and cheaper.
-
Can optimize complex assemblies rapidly, significantly reducing design costs.
-
Can manage more products simultaneously, thanks to streamlined design workflows
For an in-depth review of these topics, we invite you to explore our articles: Design automation for CAD novices and Design automation for CAD experts, as well as detailed use cases referenced in this article.
Learn more about how design automation can revolutionize your manufacturing processes, streamline workflows, and drive innovation by talking to one of our experts today.