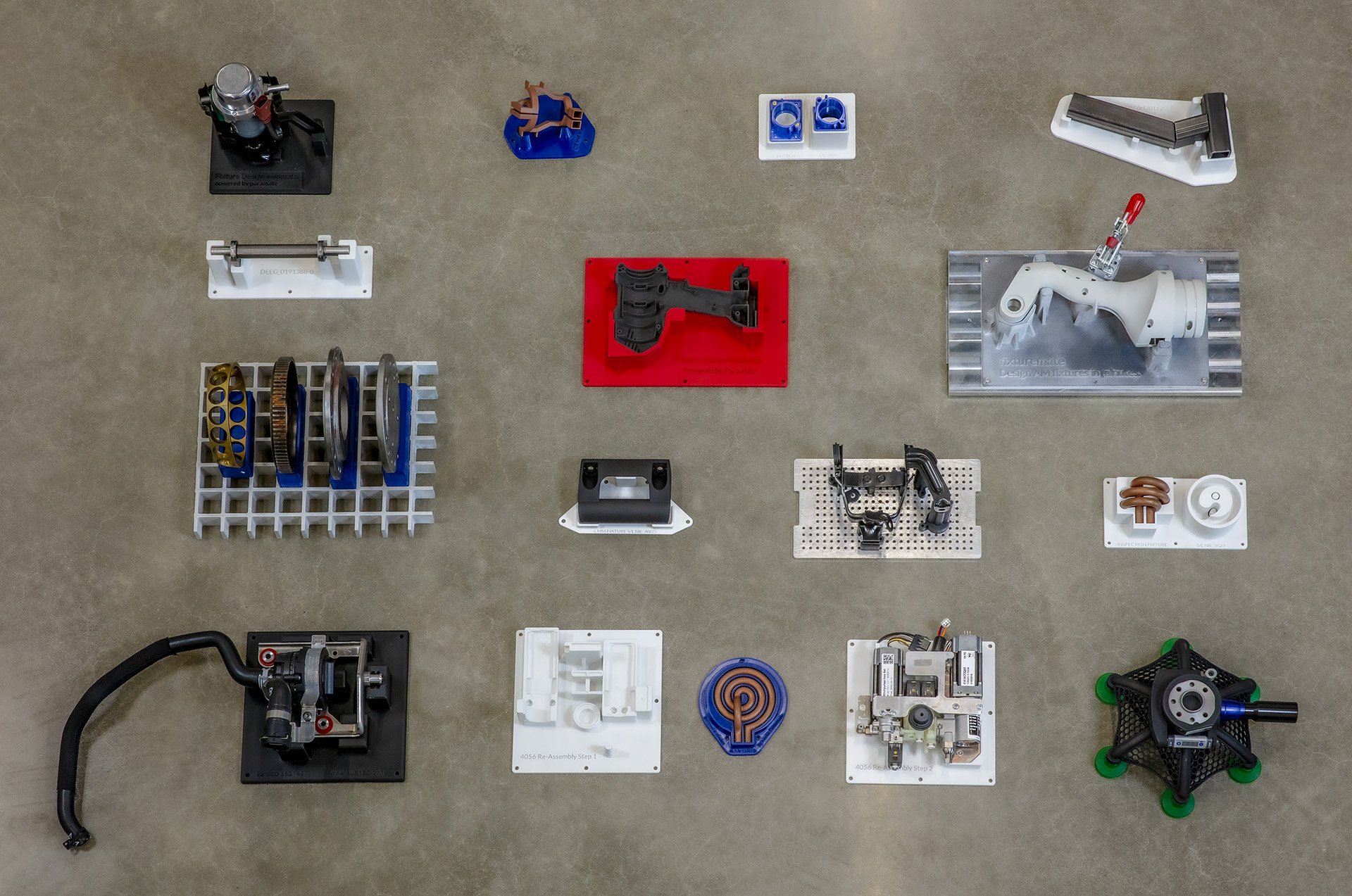
Striking a balance between speed and quality is a long-standing challenge in manufacturing. Focusing too much on speed can compromise product quality, while slow production leads to higher costs and gives competitors an advantage. Using manufacturing aids is a strategic solution: It enables manufacturers to boost production efficiency without sacrificing quality. This article explores the role of manufacturing aids, their benefits, and considerations for their effective implementation in industry.
This fixture makes automotive part assembly easier, more reliable, and consistent
Key takeaways
-
Manufacturing aids, including tools and systems like jigs, fixtures, and robotic arms, enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety in production processes.
-
They support precise, repeatable actions, improving product quality and production speed without sacrificing quality.
-
Key benefits include quick and consistent processing of production items, optimized operation accuracy, improved worker safety, and ergonomic enhancements.
-
Common types include jigs for guiding tools, fixtures for securing workpieces, gauges for measurement, and robotic arms for automated tasks.
-
Design considerations for manufacturing aids focus on cost-effectiveness, material selection, adaptability, ergonomics, maintenance ease, and compliance with industrial standards.
In this article:
Common types of manufacturing aids
Common applications of manufacturing aids
Design considerations for manufacturing aids

Manufacturing aids are essential for industry: They make operations faster, improve accuracy, improve quality of life for workers, and a host of other benefits
What are manufacturing aids?
A manufacturing aid is a tool, device, or system designed to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and safety of manufacturing and assembly processes. Manufacturing aids play an essential role in optimizing production workflows and improving product quality by supporting precise and repeatable actions.
These devices vary widely in complexity, ranging from basic tools like rulers, to highly specialized items such as fixtures or jigs. Their range extends to sophisticated technologies, including advanced robotic arms and custom software solutions, all designed to optimize operations, minimize errors, and boost productivity.
Why use manufacturing aids?
The saying "work smarter, not harder" perfectly captures why manufacturing aids are strategic assets in the world of production operations. These custom tools streamline every stage of production, making it more reliable and efficient. This, in turn, means the workers who use them can accomplish more, with higher precision and less effort.
Below are some key reasons why these tools are the backbone of effective manufacturing operations:
-
They allow production items to be processed quickly and consistently
-
They optimize the accuracy and repeatability of operations, which improves the quality of the final product
-
They solve problems specific to a bespoke component or assembly
-
They allow workers to respond quickly to problems that may arise during a manufacturing process
-
They reduce hazards and improve worker safety during operations
-
They improve worker ergonomics, making tasks more comfortable and less physically taxing
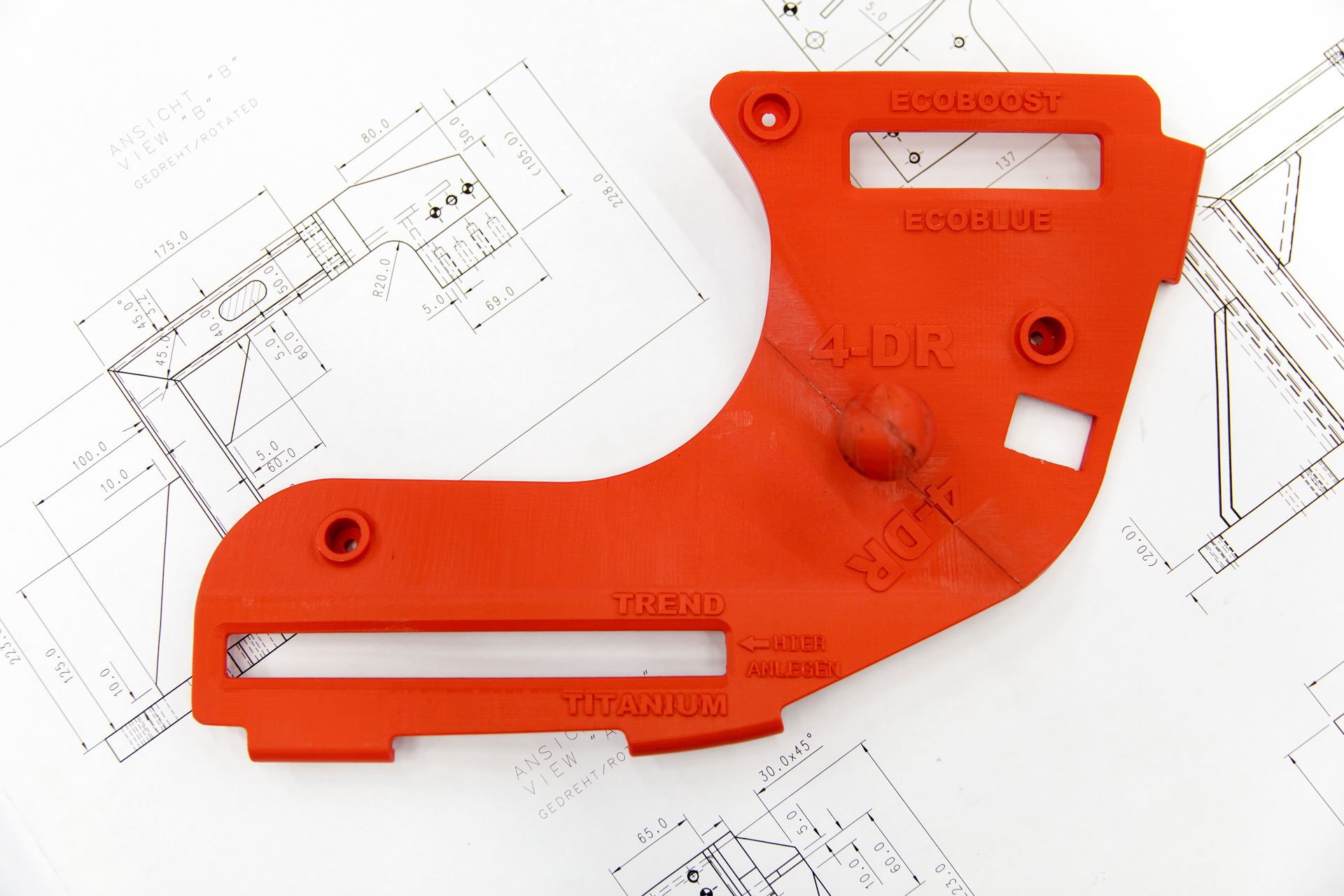

A 3D printed emblem alignment jig by Ford Motor Company
Common types of manufacturing aids
Manufacturing aids are found everywhere in manufacturing environments of all types, whether it's in a small machine shop or a large-scale industrial factory. While their applications may vary, they tend to fall into these categories:
Jigs. These are used to hold a workpiece and guide tools during an operation, ensuring precision and repeatability for tasks.
Fixtures. These are used to securely hold and support a workpiece in a specific position or orientation, so that all parts produced using it will be consistent and interchangeable.
Gauges. These are measurement tools used for checking the tolerance and dimensions of parts to ensure they meet specific manufacturing standards. They range from standard tools like calipers and micrometers to specialized, custom devices tailored for specific parts or assemblies.
Inspection gauges. These serve a broader role than regular gauges, assessing various quality aspects, including surface finish, alignment, and functionality.
Templates. These serve as patterns or models, guiding the cutting or shaping of materials to maintain uniformity in repetitive tasks.
Robotic arms and grippers. Also known as end of arm tooling, these are used in automated manufacturing processes for tasks like assembly and welding. These grippers handle materials and tools, enhancing the precision and efficiency of a process.
Manufacturing aids have a wide-ranging impact, given the consistent demand for accurate positioning and repetition in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and beyond. This is why you'll probably find jigs and fixtures are the most used manufacturing aids – they excel at meeting this essential requirement.
Common applications of manufacturing aids
Precision manufacturing
Precision manufacturing relies on achieving a high level of accuracy to produce top-quality products, and this is where manufacturing aids like jigs and fixtures come into play. They ensure parts are securely positioned, reducing errors during machining, welding, or assembly processes. They’re also instrumental for securely holding components during complex measurement procedures at the end of a manufacturing process.
Measurement and calibration tools like gauges are also useful to verify and calibrate machinery and components and to confirm that the produced parts conform to specifications. Together, these tools contribute to the quality of a manufactured product.
Assembly line optimization
Productivity is the top priority on any assembly line, as inefficiencies drive up costs. Poka-yoke, a term from Japan meaning "mistake-proofing," is a strategy that aims to reduce the potential for human error in each process. This improves the likelihood that products are put together efficiently and correctly.
Some examples of poka-yoke mechanisms:
-
Keeping workstation tools on shadow boards, so it’s clear from a quick visual inspection where each tool is, and if any necessary tools are missing
-
Color coding components or wiring to prevent incorrect assembly, and using connectors which will only work in one orientation
-
Using jigs and fixtures in assembly processes to ensure precise component positioning and guidance
A simple go-no/go gauge for inspecting inductor coils
Quality control and inspection
Products that meet customer expectations are vital qualities on any production floor. Robust quality control and inspection processes contribute a large part to this, by helping to identify and address any issues or discrepancies in the manufacturing process. Jigs and fixtures help to achieve this in multiple ways. Below are some examples:
-
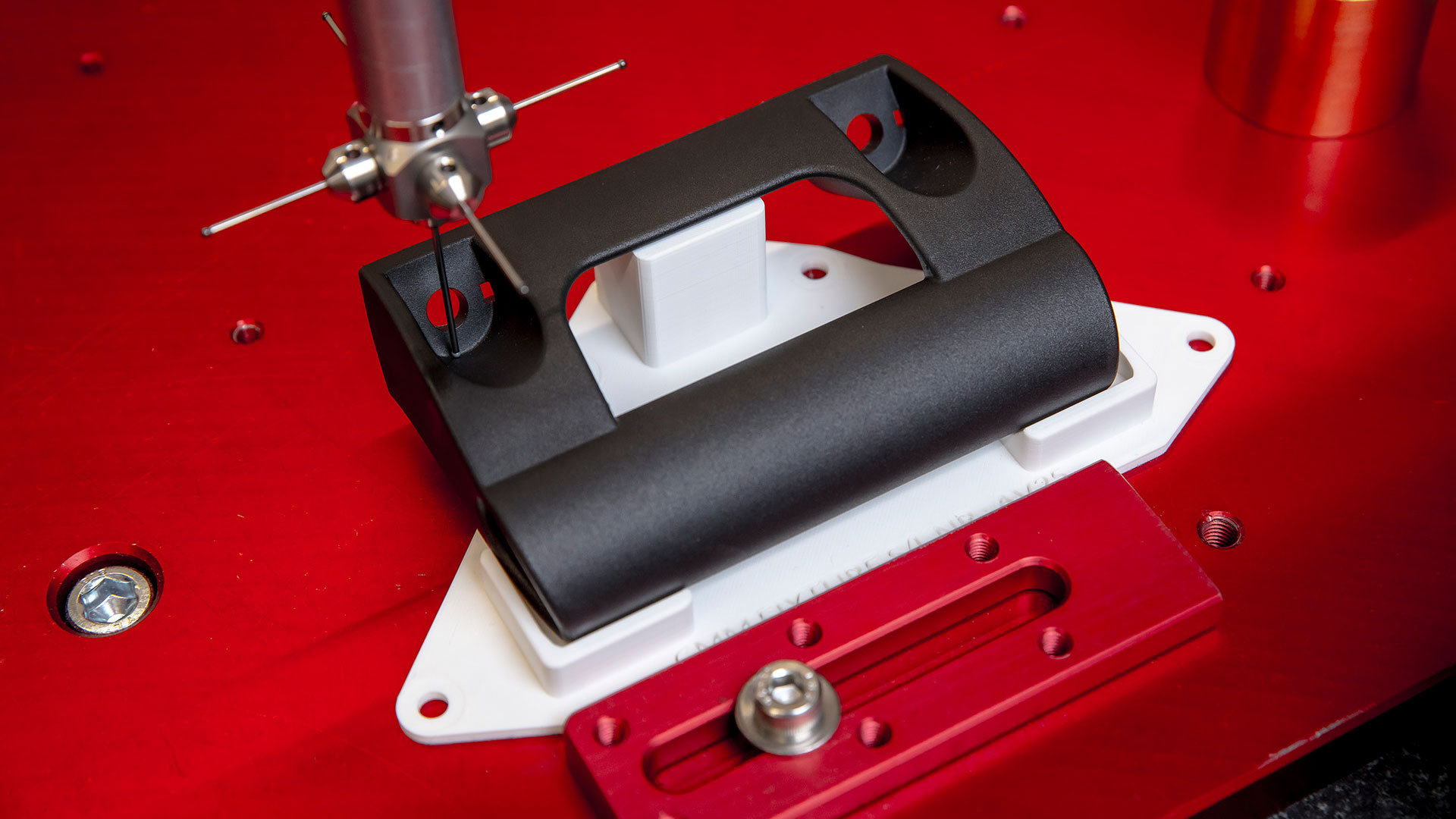
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) use precision probes and software to accurately measure the geometry of complex parts. Specialized fixtures secure workpieces to preserve the integrity of the measurements.
-
Inspection gauges, such as go/no-go gauges, help to rapidly assess part tolerances. If a part fits into the gauge, it meets the specifications; if not, it's rejected. This simplicity allows operators to conduct quality checks with minimal training.
-
Other custom gauges help to quickly calibrate and zero machinery to ensure accurate, reliable output. For instance, feeler gauges – a set of thin metal strips of varying thicknesses – are often used to measure gap widths or clearances between machine parts.
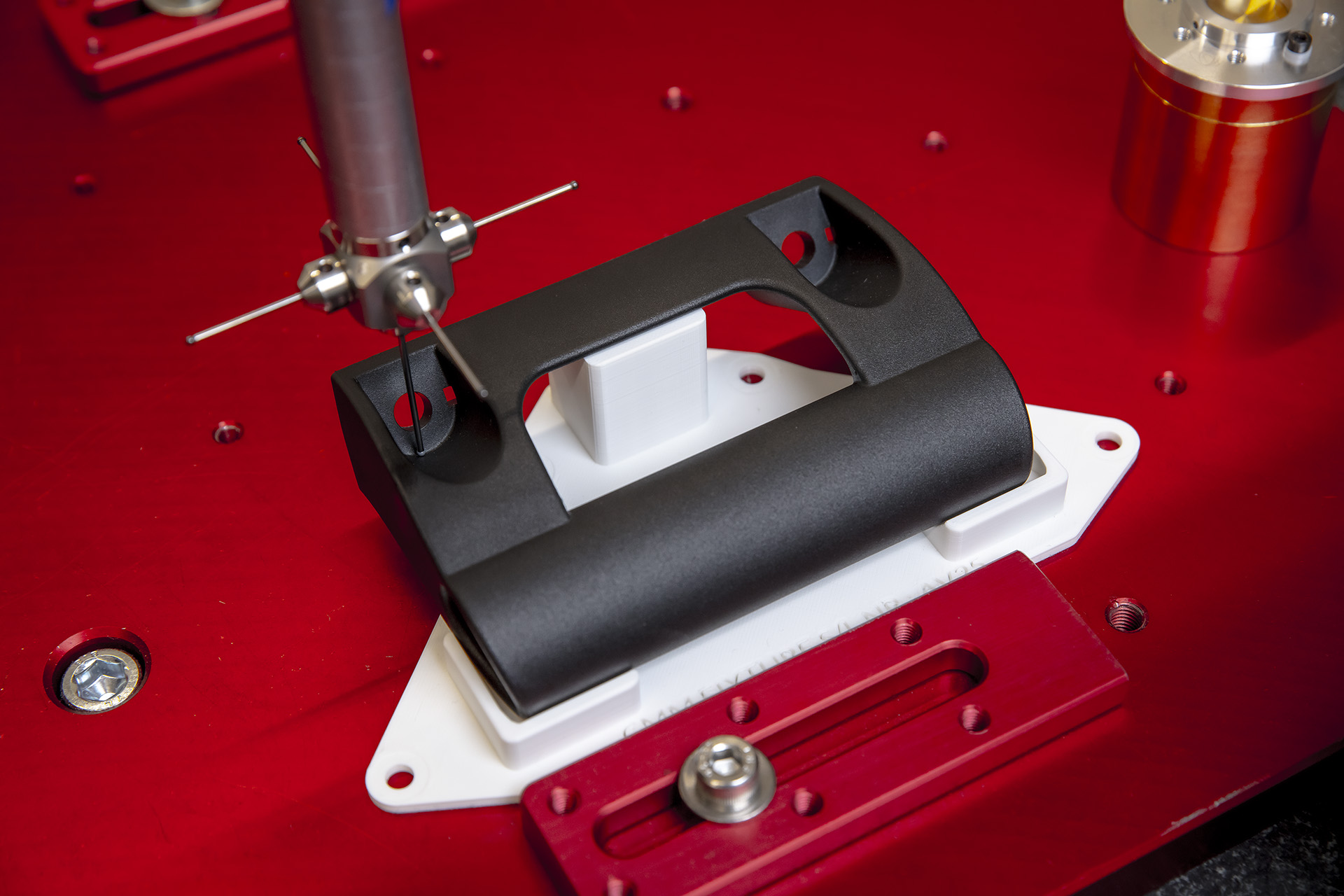
A 3D printed fixture (white) holds a workpiece firmly in place during a CMM operation
Design considerations for manufacturing aids
Cost effective manufacturing
Designing custom manufacturing aids is typically the most time-consuming part of product development, often requiring the expertise of one or more design engineers. However, it’s important to view this as an investment: The true value of their use will become evident during the product manufacturing phase, where they play a crucial role in efficiency and quality.
Design automation solutions such as fixturemate offer proven methods to speed up this design process. fixturemate software expedites repetitive manual CAD tasks, making design accessible for people who haven’t used CAD before.
CAD tasks like creating the negative of free-from surfaces are time consuming and challenging for engineers. fixturemate makes operations like this simple using design automation
Fixtures are typically highly customized items produced in low volumes, so selecting the appropriate manufacturing method is critical. For example, if only ten units of a design are needed, injection molding is not a practical choice; this method is better suited for mass production scenarios involving thousands of units and upfront costs for designing and producing tooling.
3D printing is an increasingly adopted solution for highly customized, low-volume items. fixturemate is specifically designed to integrate with a 3D printing workflow, and enables anyone to quickly design and enhance manufacturing aids – even without CAD skills. With fixturemate, a design can be 3D printed in a matter of hours, outpacing traditional methods that often have a lead time of weeks before a design can be rolled out on the production floor.
A 3D printer can produce parts locally in a matter of hours, minimizing lead times that traditionally take weeks
Material selection
Manufacturing aids are integral to repeatable processes, designed to withstand hundreds or thousands of uses. It's crucial that the materials selected for these manufacturing aids are robust and durable enough to endure industrial environments. For instance, certain 3D printing materials may offer superior impact resistance, while others excel in temperature tolerance. This diversity in material properties highlights the importance of choosing the right materials for manufacturing aids to ensure their longevity and effectiveness in specific applications.
For fixtures designed for short-term use, like a one-time small batch, 3D printing allows for the reprocessing of old fixtures into new ones. Choosing a recyclable 3D printing material ensures these parts can be recycled after their temporary application.
Adaptability to different scenarios
Equipment and tools should be able to be changed to fit different needs. This is important because it helps them to remain useful even when the requirements change. For example:
-
A modular assembly line can be adjusted to produce different types of products without significant retooling. This adaptability allows the production line to remain efficient and cost-effective when switching between various product lines or responding to changes in market demand.
-
Adjustable gauges in quality control can be easily modified to measure different dimensions or specifications, making them versatile tools for ensuring product quality across various production runs.
-
Adjustable clamps can be customized to hold different shapes and sizes of workpieces securely. This flexibility reduces the need for multiple specialized clamps and simplifies the production process.
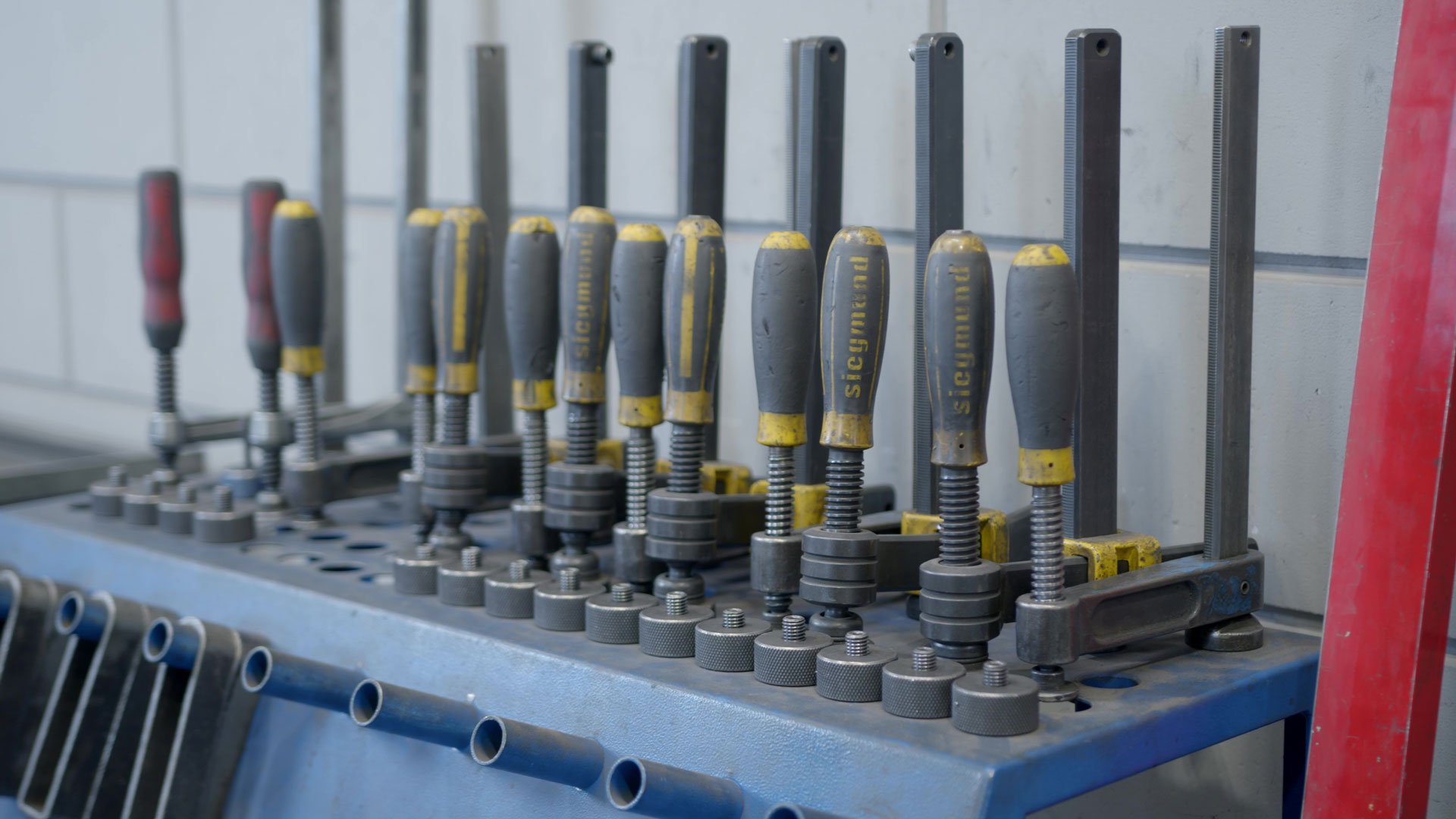

Welding clamps are an example of manufacturing aids
Ergonomics
Ensuring the operator's comfort and ease of use is a priority. When manufacturing aids are designed with the operator in mind, it not only improves their efficiency but also reduces the risk of operator fatigue and errors. Prioritizing ergonomics creates a safer and more productive work environment, ultimately leading to better manufacturing outcomes.
fixturemate is a useful solution here, because workers who will be using the tools on the production floor are empowered to design and improve the tools they will be using, enhancing ergonomics and ease of use, amongst other things.
Using 3D printing for manufacturing aids can enhance ergonomics, as 3D printed polymers are lighter and easier to handle than metal counterparts yet remain durable for effective use in manufacturing settings.
Maintenance
Manufacturing tools should be designed for straightforward maintenance, cleanliness, and inspection. Making their upkeep simple ensures quick repairs or adjustments, reducing downtime in production. Cleanliness is especially important in sectors with strict hygiene standards, so it's crucial these tools are easy to clean.
Easy inspection allows for quick identification of wear, damage, or issues, ensuring the tools work correctly and safely. Regular checks help avoid potential problems, ensuring smooth operation. By focusing on these design elements, manufacturers can improve efficiency, safety, and product quality.
Compliance with industrial standards
Unsafe manufacturing aids can lead to accidents, injuries, and even production delays. It’s imperative to prioritize safety throughout the design process.
In certain scenarios, manufacturing aids may also need to be certified for compliance with industry-specific safety standards. Certification provides an additional layer of assurance that the manufacturing aids meet the required safety criteria and can be safely used in the intended manufacturing environment. It is a crucial step to demonstrate reliability and suitability for their intended tasks, particularly in industries where safety regulations are stringent, such as aerospace or healthcare.
By placing safety at the forefront of aid design and, when necessary, obtaining the requisite certifications, manufacturers not only protect their workforce but also safeguard the integrity of their production processes. This proactive approach not only minimizes the risk of accidents but also contributes to a smoother and more efficient manufacturing operation.

Supporting an industry
Manufacturing aids play a crucial role in the world of production operations, helping businesses improve efficiency, accuracy, safety, and product quality. Even though they might not grab the spotlight, their impact is significant, forming the foundation of manufacturing excellence.
At trinckle, we have a special focus on fixtures among manufacturing aids. If you want to speed up fixture production, you'll find valuable insights in our article Fixtures in Modern Manufacturing. And if you're interested in designing your own fixtures without CAD skills – visit our fixturemate page, where you can easily create fixtures that work for your business.
Explore related articles

Design automation in use: Measuring fixtures
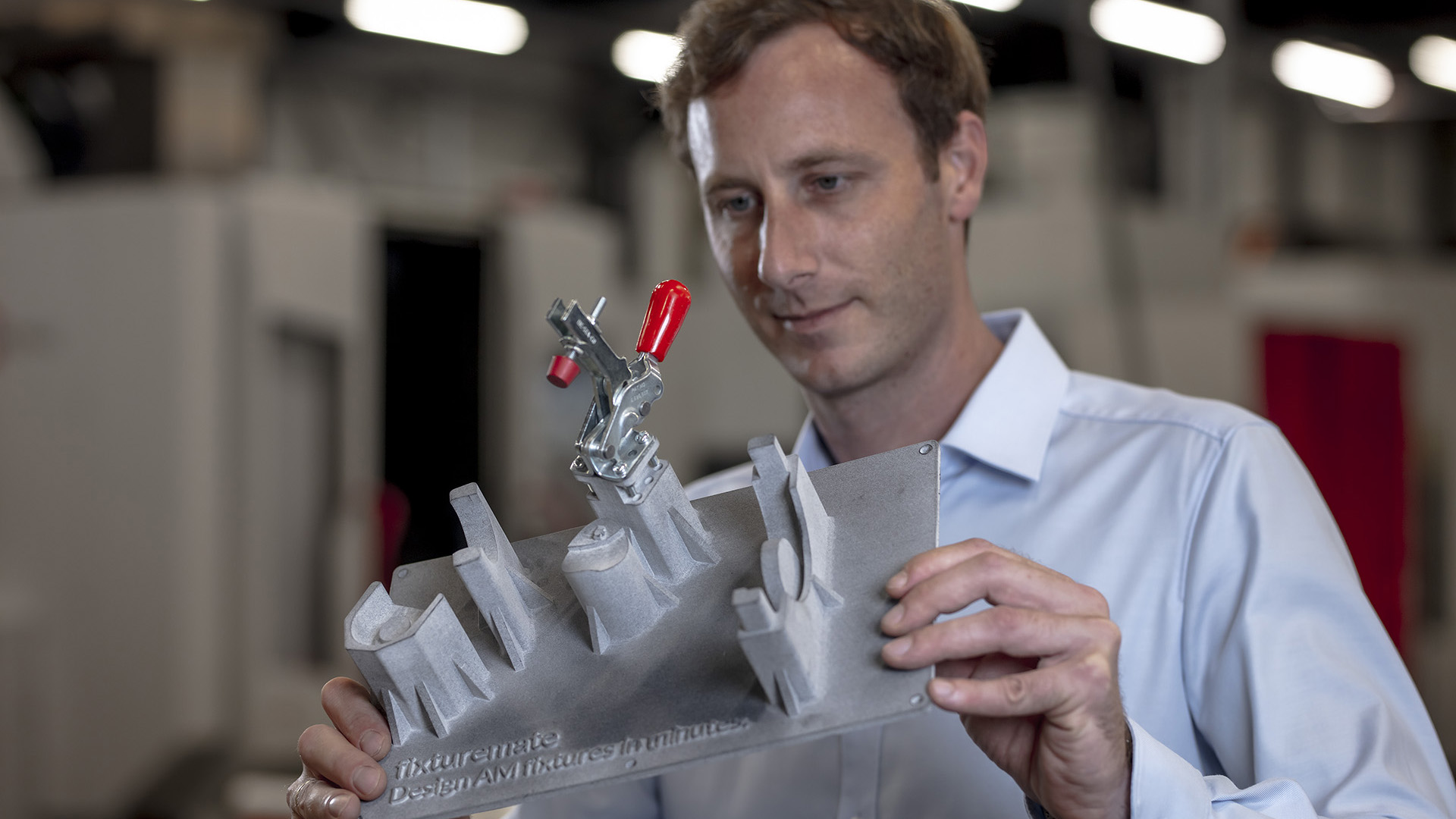
Fixtures in modern manufacturing

